All Dinosaurs
 Dinosaurs refer to only one group of lizards or presumptive (reptiles) who lived in a mesosis in the middle of life on Earth.
Dinosaurs refer to only one group of lizards or presumptive (reptiles) who lived in a mesosis in the middle of life on Earth.
At the same time, there were other groups of prestiges, such as flying and cro-odile lizards, snakes and flats, fishermen and lizards, and reptiles of mammals.
The range of differences between dinosaurs was so large that kinship relations between them were very difficult. They could be the size of a cat or a chicken, and they could have reached the size of a huge whale.
Some of them moved on four limbs, and others ran on their back legs.
There were hunters and bloodthirsty predators among them, but there were hopeless plant animals.
But one of the most important features that characterize all of their species is staring into the eyes: they were all terrestrial animals!
Their limbs were located at the bottom of the hull, not at the side, like most presumptive.
So dinosaurs can also be described as running lizards. 2
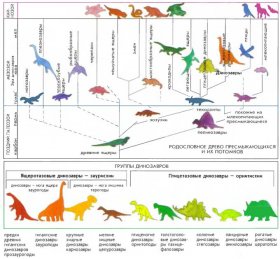
A total of over 10,000 dinosaurs residues were found: individual bones and whole skeletons, skulls and teeth, eggs and excrements, covering traces and other prints.
All information on dinosaurs currently available to scientists is obtained through the study of these residues.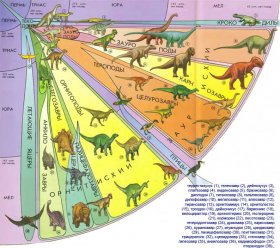 In more than 150 years of study of fossils, paleontologists have been able to identify and describe more than 500 different types of dinosaurs, but all new discoveries are constantly being reported.
In more than 150 years of study of fossils, paleontologists have been able to identify and describe more than 500 different types of dinosaurs, but all new discoveries are constantly being reported.
It also happens that someone finds occamenality and represents them as a new type of dinosaur, and then, as a result of research, it finds out that they belong to an already known species, and that new name has to be refused.
It also happens that for different species, males and females or young and adult animals of the same species are misappropriated.
Some of the 500 known dinosaurs have so close kinship among themselves that they are united into a single family.
For example, nine species of horn dinosaurs now belong to the triceratos family (with three horns on the head) and three species of long-distance giant dinosaurs from North America and North and East Africa are part of the Brahiosavre family (lent lizards).
Giant dinosaurs form over 40 families. The largest groups are Predatory dinosaurswith more than 150 families and two limbs of bird dinosaurs comprising 65 families.
The smallest species appears to be a group of bulging dinosaurs, where only eleven families are known to date.